Product Update - v22.34
Improvements and Updates
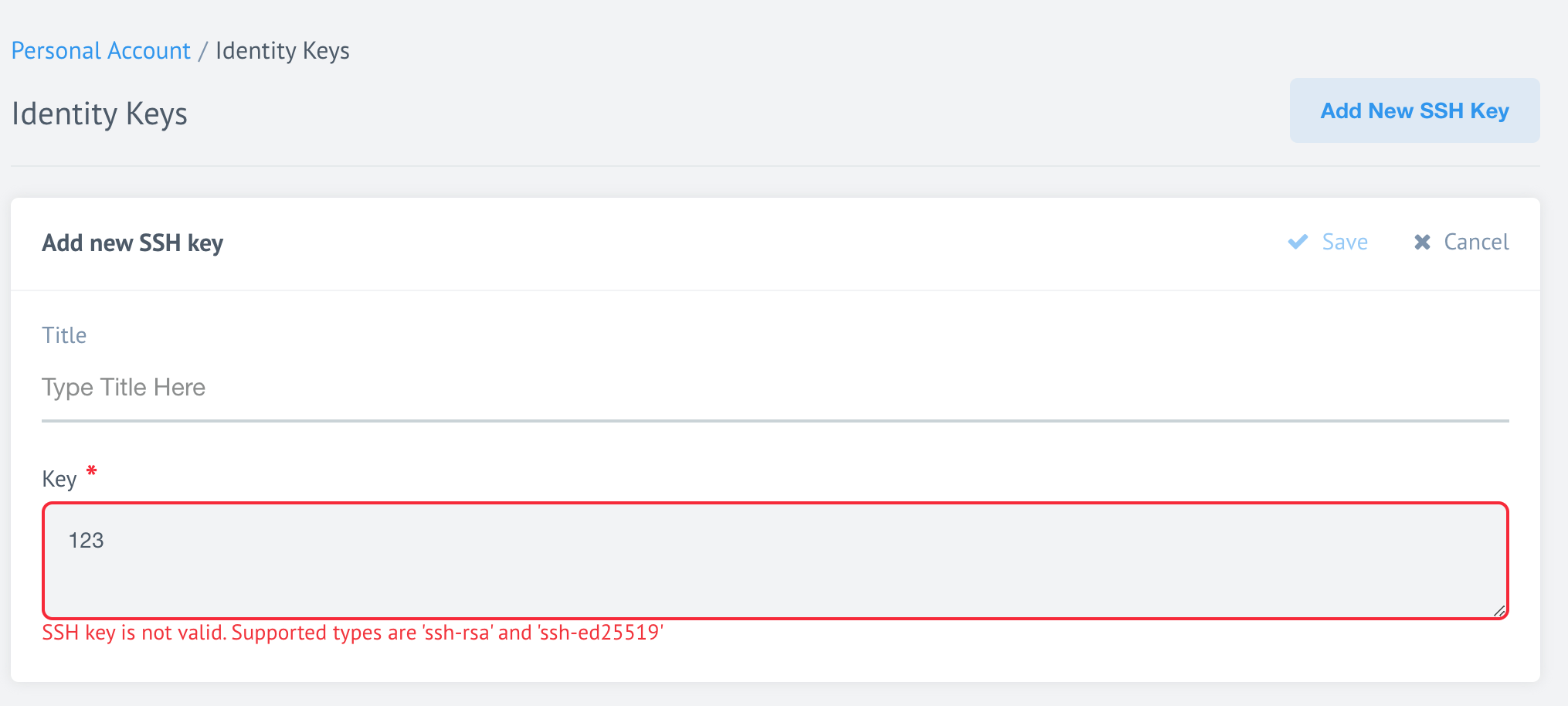
Informative error messaging for invalid SSH key entries
When we introduced support for newest SSH versions
for the user SSH keys used to deploy components, we deprecated the old ssh-dss
types. If users enter an unsupported or incorrect SSH the user interface now
displays an informative error message instead of simply disabling the ‘Save’ button.
Deployment of Externally Build Dockers
This capability will provide an alternative to Git push deployment of user developed components and is of interest to enterprise clients wishing to condense entire integration flows into single custom components and maintain control at the docker level.
At this earliest stages we lay our groundwork by updating the component
commons and api to support components pull from external docker registries.
The following new attributes were added:
docker_registryobject into the HTTPPOSTcall to/v2/teams/attributes.docker_registry.uri- Docker Registry URIattributes.docker_registry.credentials- Docker Registry credentials
docker_repo_nameanddocker_target_tagin thePOSTHTTP call to/v2/components(can be set if its team hasdocker_registryobject)attributes.docker_repo_name- String representing component’s name in docker registry. Available only if team supports docker registryattributes.docker_target_tag- String representing component’s tag in docker registry. Available only if team supports docker registry
Please note, as of this stage these attributes have no functionality attached to them.
HELM3
We constantly improve different aspects of HELM3 deployments in collaboration with our partners. This section lists updates and improvements included in this release.
Dashboard Runlog retention period
The flow execution statistics presented on the Dashboard Runlog are stored in the platform Mongo Database. This is in contrast to the flow execution threads, shown on the Executions pages, which are stored separately in Clickhouse.
When you access the Dashboard Runlog, the platform queries the MongoDB to get these records. These database calls can delay display of the runlog for users with many active flows. To enable users to manage such circumstances we have added an environment variable which defines the retention period of runlogs in the database.
Previously you could only control the retention period by enforcing the expireAfterSeconds
option in the Database index holding the execution records. In this release we
introduce a new TASK_STAT_START_INDEX_TTL environment variable to the HELM3 charts,
which you can use to set retention suitable for your environment. It is mandatory
that a value is set for TASK_STAT_START_INDEX_TTL and the
default value is set at 432000 seconds (5 days). Which means the platform
will store the Dashboard Runlog records for 5 days in the Database.
Breaking Changes
Setting the TASK_STAT_START_INDEX_TTL environment variable to control the retention
period of the Dashboard Runlog is recommended for the new installations of the platform.
If your platform installation already has the retention period set in the Database prior to your installation of the platform 22.34 version then your environment variable will not be applied. If you need to change the value you must change the Database index setup prior to the deployment of the current release.
If you need to change the retention period of Dashboard runlogs in the future, remove
the expireAfterSeconds option of the Database index containing the Dashboard Runlog records,
set the value of TASK_STAT_START_INDEX_TTL environment variable and then deploy
the platform version again.
Kubernetes 1.22
Our platform is now compatible with the Kubernetes version 1.22. Check out the
new features enabled here.
MongoDB Transport Layer Security verification is enforceable
You can now enforce MongoDB TLS verification in all platform services by using newly introduced HELM3 chart configurations:
.Values.global.secrets.mongodbTlsCertificateKey- secret name with the TLS certificate and key. If specified, will be mounted to the services and specified in thetlsCertificateKeyFileconnection option..Values.global.secrets.mongodbTlsCA- secret name with CA certificate to validate MongoDB server certificate on the client side. If specified, will be mounted to the services and specified in thetlsCAFileconnection option.
OEM Related
Information in this section is intended for our customers who use the OEM version of the elastic.io platform.
Embedded credential management for OEM End Users
Here we present further improvements to the recently introduced White-label credential management feature. Now you can use HTML inline frame or iFrame to embed the credentials.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Embedded Credentials Demo</title>
<style>html, body, iframe { height: 85%; width: 90%; margin: 0;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src="https://[eio_platform_domain]/embedded-credentials/[repoId]?workspaceId=[workspaceId]&ssoProviderType=[ssoProviderType]&ssoProviderId=[ssoProviderId]" />
</body>
</html>
The embed URL construction scheme is the same. Refer to the 22.20 release for details.
Pleass Note: End Users must enable pop-ups in their browser settings in order to use the embedded credential management.
Fixed bugs
- Fixed the bug when an HTTP
POSTto/v2/workspaces/:id/secrets/:id/refreshendpoint would return outdatedaccess_tokeninstead of the newly refreshed value.
Components
Qualtrics component 1.0.0
- ADDED
Get New and Updated Objectspolling trigger - ADDED
Make Raw Requestaction - ADDED
Upsert Objectaction - ADDED
Generate Custom Distribution Linkaction - ADDED
Getting Survey Responsesaction - ADDED
Lookup Object (at most one)action
Google Spreadsheets V2 component 1.0.1
- IMPROVED the component behavior in case of
429status code. Now it will retry the messages with an exponential backoff. - IMPROVED the component behavior in case of
5xxerrors. The messages will be retried with an exponential backoff as well.
SFTP component 1.5.1
- UPDATED component the
component-commons-libraryto the version3.0.1
SugarCRM component 1.1.6
- ADDED
email1andemail2fields for metadata of Contacts module in theUpsert Action - UPDATED
elasticio-sailor-nodejstov2.6.29
Shopware V6 component 1.0.0
- ADDED
Make Raw RequestAction
Request-Reply component 1.2.5
- UPDATED the
maester-clientlibrary version to4.0.2 - UPDATED the
component-commons-libraryto the version3.0.1
Zoho Subscription component 2.0.0
- UPGRADED authentication mechanism to
OAuth 2.0and migrated to the Secrets service - UPDATED the sailor library to version
2.6.29 - UPDATED build time dependencies